
Age significantly affects exercise needs and capabilities, with different age groups requiring tailored exercise regimens to optimize health benefits and accommodate physiological changes You can try to incorporate exercise into your daily life by scheduling a session in your calendar, committing to exercising with someone else, or trying to avoid sitting for long periods of time What are the benefits of regular exercise?. Here’s a detailed look at how age influences exercise requirements and abilities:
Children and Adolescents (5-17 years)
Children and adolescents should engage in at least 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity daily. This activity should include:
-
- Aerobic exercises: Activities like running, swimming, and cycling.
-
- Muscle-strengthening activities: Exercises such as climbing or push-ups at least three days a week.
-
- Bone-strengthening activities: Activities like jumping and running at least three days a week.
These activities support natural development, enhance physical and mental health, and help establish lifelong healthy habits
Young Adults (18-64 years)
For adults aged 18 to 64, the recommended exercise regimen includes:
-
- Aerobic activity: At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, spread over several days.
-
- Strength training: Exercises targeting all major muscle groups on at least two days a week.
-
- Flexibility exercises: Activities like yoga or stretching to maintain flexibility and prevent injuries.
Regular physical activity in this age group helps prevent chronic diseases, maintain a healthy weight, and improve mental health
Older Adults (65 years and above)
Older adults should focus on maintaining physical function and preventing falls. Recommendations include:
-
- Aerobic activity: At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
-
- Strength training: Muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week.
-
- Balance exercises: Activities like tai chi or balance training exercises at least three days a week to prevent falls.
-
- Flexibility exercises: Regular stretching to maintain joint mobility.
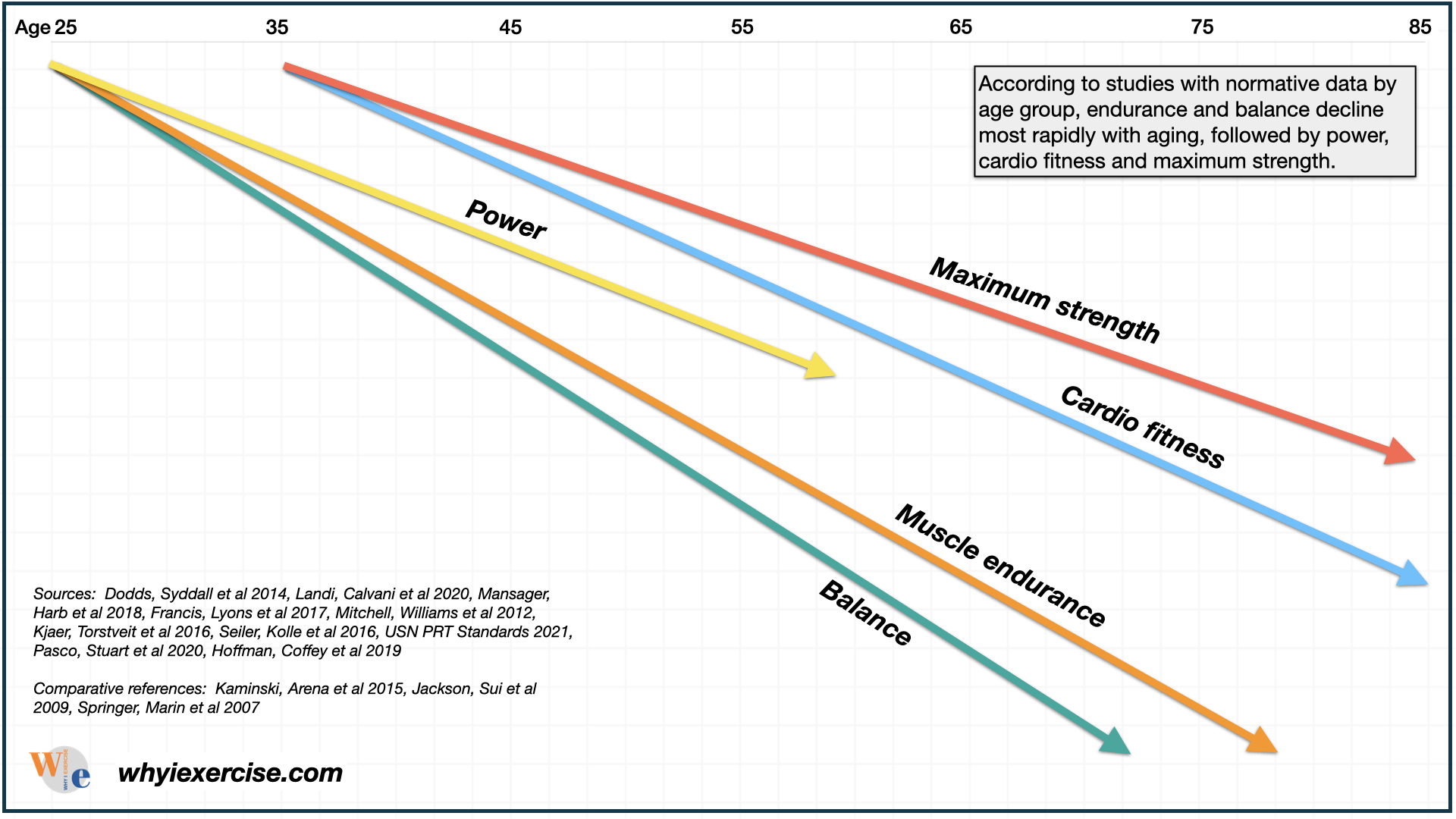
Exercise in older adults can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve mental health, and enhance overall quality of life. It also helps mitigate age-related declines in muscle mass and strength, known as sarcopenia.
Age-Related Changes and Considerations
Muscle Mass and Strength
-
- Young Adults: Peak muscle mass and strength are typically achieved in the 20s and 30s. Regular strength training is crucial to maintain these levels.
-
- Middle Age: Muscle mass and strength begin to decline in the 30s and 40s. Resistance training becomes increasingly important to slow this decline.
-
- Older Adults: Significant muscle loss can occur, leading to decreased functional ability. Strength training and protein intake are essential to combat sarcopenia.
Cardiovascular Fitness
-
- Young Adults: High-intensity aerobic activities can enhance cardiovascular fitness.
-
- Middle Age: Cardiovascular efficiency may decrease, necessitating regular aerobic exercise to maintain heart health.
-
- Older Adults: Aerobic capacity declines, but regular aerobic exercise can still significantly improve cardiovascular health and overall fitness
Flexibility and Balance
-
- Young Adults: Flexibility exercises help prevent injuries and maintain range of motion.
-
- Middle Age: Flexibility may decrease, making regular stretching important.
-
- Older Adults: Balance exercises are crucial to prevent falls, a common issue in this age group.
Psychological and Cognitive Benefits
Regular exercise across all age groups has been shown to improve mental health, reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, and enhance cognitive function. These benefits are particularly pronounced in older adults, where exercise can help slow cognitive decline.
In summary, while exercise needs and capabilities change with age, staying active is crucial at every stage of life. Tailoring exercise routines to fit age-specific requirements can help maintain physical health, improve mental well-being, and enhance overall quality of life.